Cloud computing is the on-demand access to a wide range of computing resources—such as physical and virtual servers, data storage, networking capabilities, application development tools, software, and AI-powered analytic tools—delivered over the internet with pay-per-use pricing. This model offers unparalleled flexibility and scalability compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Cloud computing has become an integral part of daily life, whether it’s accessing a cloud application like Google Gmail, streaming a movie on Netflix, or playing a cloud-hosted video game.
In business settings, cloud computing is indispensable, benefiting organizations from small startups to global enterprises. It enables remote work by making data and applications accessible from anywhere, supports seamless omnichannel customer engagement, and provides the computing power needed for advanced technologies like generative AI and quantum computing.
Cloud services providers (CSPs) manage these technologies, typically offering them on a pay-as-you-go or subscription basis.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Compared to traditional on-premises IT, where companies must own and maintain physical data centers and servers, cloud computing offers numerous advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing eliminates the need to purchase, install, configure, and manage expensive on-premises infrastructure. You only pay for the resources you use.
- Speed and Agility: Cloud services enable the use of enterprise applications within minutes, empowering development teams to quickly leverage cloud-based software and infrastructure.
- Unlimited Scalability: Cloud computing provides elasticity and self-service provisioning, allowing you to scale capacity up or down based on demand, spreading applications globally to users.
- Enhanced Strategic Value: Organizations can leverage the latest technologies to gain a competitive edge. For example, AI-powered virtual assistants in customer-facing industries can improve response times and free up staff for higher-level tasks.
Origins of Cloud Computing
The concept of cloud computing dates back to the early 1960s when Dr. Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider envisioned a global network, later known as the Intergalactic Computer Network. Modern cloud infrastructure began to take shape in the early 2000s. In 2002, Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched its first cloud-based storage and computing services, followed by the introduction of Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) in 2006. That same year, Google launched Google Apps (now Google Workspace), and Microsoft introduced its SaaS application, Microsoft Office 2011.
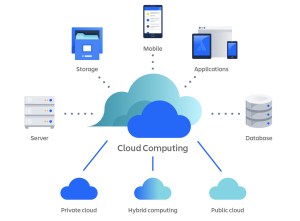
Cloud Computing Components
Modern cloud computing architecture consists of several integral components:
- Data Centers: CSPs own and operate data centers housing servers, storage systems, and other hardware forming the cloud’s physical foundation.
- Networking Capabilities: High-speed networking connections, including WAN, load balancers, CDNs, and SDN, ensure quick and secure data flow between users and cloud resources.
- Virtualization: By abstracting IT infrastructure through virtualization, cloud providers maximize resource utilization, allowing multiple virtual servers on a single physical server.
Cloud Computing Services
Cloud services are categorized into four main models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Rent IT infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Provides an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing applications.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Serverless Computing: Focuses on app functionality without the need to manage servers and infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud services can be deployed in three main models:
- Public Cloud: Owned and operated by third-party providers, delivering resources over the internet.
- Private Cloud: Exclusive to a single organization, either hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
- Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between them for greater flexibility and optimization.
Uses of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is prevalent across various domains:
- Creating Cloud-Native Applications: Build and scale web, mobile, and API applications quickly.
- Data Storage and Recovery: Securely store and back up data, accessible from any location.
- Streaming: Deliver high-definition video and audio globally.
- Software Delivery: Offer the latest software versions and updates on demand.
- Application Testing and Development: Scale development environments up or down as needed.
- Data Analysis: Use cloud services for machine learning and AI to derive insights.
- Embedded Intelligence: Engage customers and gain insights through intelligent data models.
In summary, cloud computing is revolutionizing how businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources, driving innovation, efficiency, and strategic growth across industries.