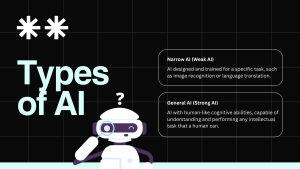
What is Artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a digital technology capable of thinking like human intelligence and helping humans and machines solve many problems. AI technology can process large amounts of data in less time than humans.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can function on its own or in conjunction with other technologies (such as sensors, geolocation, and robotics) to accomplish tasks that would typically require human intelligence or intervention. Artificial intelligence (AI) is present in everyday news and life in a number of ways, including digital assistants, GPS guidance, driverless cars, and generative AI tools like Open AI’s Chat GPT.
Natural language processing and deep learning are frequently mentioned in conjunction with artificial intelligence, which is a branch of computer science. The goal of these fields is to create artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that, like the human brain, can “learn” from data and, over time, produce predictions or classifications that are ever more accurate.

Despite the many hype cycles surrounding artificial intelligence, even detractors seem to agree that ChatGPT’s release represents a sea change. The previous time generative AI was this significant, advances in computer vision led the way; this time, natural language processing (NLP) is leading the way. In addition to human language, generative AI has the ability to learn and synthesize various data types such as images, videos, software code, and even molecular structures.
The uses of AI are expanding daily. However, as the excitement surrounding the application of AI technologies in business grows, discussions about responsible AI and AI ethics become vitally important. For more details on this topic visit AI category of techcyb.

A history of how Artificial intelligence originated.
1950: Alan Turing, widely regarded as the “father of computer science” for his role in breaking the German ENIGMA code during WWII, publishes Computing Machinery and Intelligence. In this seminal paper, Turing poses the question, “Can machines think?” He introduces the concept now known as the “Turing Test,” where a human tries to distinguish between responses from a computer and a human. Though the test has faced criticism over the years, it remains a foundational concept in the history of AI and continues to influence discussions around linguistics and philosophy.
1956: John McCarthy coined the term “artificial intelligence” at the first AI conference held at Dartmouth College. McCarthy, who later invented the Lisp programming language, was joined by Allen Newell, J.C. Shaw, and Herbert Simon, who created the Logic Theorist, the first AI software program.
1967: Frank Rosenblatt developed the Mark 1 Perceptron, the first computer model based on a neural network capable of learning through trial and error. However, in 1968, Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert published Perceptrons, a critical work that temporarily dampened enthusiasm for neural network research.
1980s: Neural networks make a comeback with the introduction of the backpropagation algorithm, which has become widely used in AI applications.
1995: Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig publish Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, a leading AI textbook that distinguishes between AI systems based on rationality and thinking vs. acting.
1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats world chess champion Garry Kasparov in a highly publicized match, marking a significant milestone in AI.
2004: John McCarthy publishes What Is Artificial Intelligence?, offering a definition that continues to be widely referenced in AI discussions.
2011: IBM Watson defeats champions Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter on Jeopardy!, showcasing AI’s potential in natural language processing.
2015: Baidu’s Minwa supercomputer, using a convolutional neural network, outperforms humans in image recognition, highlighting advancements in deep learning.
2016: DeepMind’s AlphaGo, powered by a deep neural network, defeats world champion Go player Lee Sedol in a five-game match. This victory is notable for the immense number of possible moves in Go, which surpasses 14.5 trillion after just four moves. Google later acquires DeepMind for around $400 million.
2023: Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT revolutionize AI, driving significant enterprise value. These generative AI models are pre-trained on vast amounts of raw, unlabeled data, leading to unprecedented improvements in AI performance.